Explore our comprehensive sales funnel guide, covering its stages and advice on constructing an effective sales strategy to boost your brand’s sales efforts.
What is a sales funnel?
A sales funnel is a marketing term used to capture and describe potential customers’ journeys, from prospecting to purchase. A sales funnel consists of several steps, the actual number of which varies with each company’s sales model.
Well-built sales funnels without gaps allow companies to shepherd potential customers through the buying process towards purchase completion. By contrast, those funnels with gaps will lead to potential customers dropping out of the sales process, like water flowing through a sieve.
Why is the sales funnel important?
A sales funnel helps marketers understand a customer’s purchasing journey while identifying the stage of the customer’s journey. These insights can be used to decide which marketing channels and activities will best guide the customer towards a purchase.
A sales funnel also allows marketers to tailor and optimise their activities and messaging to increase conversions.
So, how does a sales funnel work?
As the name suggests, a sales funnel takes in many leads and prospects and narrows them down towards the bottom, giving you fewer paying customers. While the specifics of the sales funnel differ from industry to industry, in fact, even from company to company, we can understand how it works with a simple example of a B2C sales funnel for an e-commerce website.
A potential customer for the site will start their journey as a visitor: someone who might visit the site by clicking on a Google search result, social media post, or advert. When they visit and browse the website, they might (and should) be offered a chance to sign up for the e-commerce site’s email list. If they do, they become a lead.
Depending on their contact details, they can be engaged through various channels such as email, text, and phone. Their interaction with these marketing campaigns will likely nudge them to return to the e-commerce website to browse relevant products or special offers, turning them into prospects.
From prospect to customer, it is a matter of incentivising them enough with product offerings, messaging, or even a simple coupon code.
The 6 stages in a sales funnel
Again, it’s important to note that not all companies’ sales funnels will have six levels or stages. Sales funnels vary in size and shape from company to company and industry to industry.
Some businesses may operate on a traditional sales funnel like an AIDA model (Awareness, Interest, Desire/Decision, Action). Others may use a modern sales funnel like the flywheel model (Attract, Engage, Delight), popularised by Jim Collins’s Good to Great book. Others still may have more niche sales funnel templates for a specific purpose, such as a conversion funnel to convince a customer to sign up for an event or back an upcoming product launch.
However, a basic sales funnel can be described as consisting of six levels. Marketers can take inspiration from this basic structure to design a sales funnel that suits the needs of their organisation.
1. Awareness
At the very top of the sales funnel is the awareness stage, which is populated by the largest number of people. These people, not quite ready to be prospects yet, have just had their first interactions with your company and its offerings. They don’t know much about your brand but know it exists.
- Examples include:
- Blog posts
- Infographics
- Social media updates
- Paid advertising (e.g., Facebook Ads)
2. Interest
The first interactions will hook some newly aware people and draw them slightly deeper into the funnel. With their interest piqued, these people will spend some time getting to know more about your company and your offerings. They might browse your website or catalogue, read your blogs, or peruse reviews from past customers.
- Examples include:
- Whitepapers
- Webinars
- Industry reports
- Educational materials hosted on a content hub
3. Evaluation
Armed with knowledge gathered during the interest stage, your prospects will double down on their efforts to know more about your company and offerings better. They may contact your customer service team with specific questions or fill out a form to access more information.
- Examples include:
- Case studies
- Product demos
- Customer stories
- Social proof (reviews and testimonials)
Remember, by this stage, they may have already compared your offerings to those of your competitors. So, it is important to answer their questions and help them understand how your offerings can solve their problems or needs.
4. Negotiation and decision
The prospect has almost decided to purchase your product or service. Depending on the nature of your offerings, they might begin a negotiation over the price, terms of purchase, or both. But it’s fair to assume they have a purchase intention.
- Examples include:
- Detailed product comparisons
- Pricing guides
- Customised offers
- Negotiation support content
5. Sale
We’ve reached the bottom third of the sales funnel. The prospect and seller have negotiated the terms of the sale to their mutual satisfaction, and the prospect pays the seller to become a buyer officially.
- Examples include:
- Clear calls-to-action
- Straightforward checkout processes, including easy credit card payments
- Automation software to streamline the purchase process
6. Renewal or repurchase
The sale stage is not the end of the sales funnel. Soon, the sales contract will be renewed. The customer must now decide whether to continue with the same seller. If so, there might be a fresh round of negotiations over price and purchase terms, followed by a renewal or repurchase.
- Examples include:
- Implementing customer success programs
- Personalised experiences
- Loyalty programs
- Win-back campaigns (re-engagement and reactivation campaigns)

As mentioned earlier, many companies may not experience a sales funnel like the one described above. Many purchase journeys might end at the ‘sale’ stage, while others might be complex enough to warrant even more steps. The above framework, however, is broadly applicable to most business models.
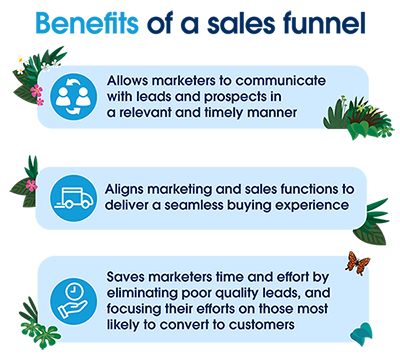
Benefits of a sales funnel
A well-defined sales funnel can offer several benefits to your company:
1. Relevant and timely messaging
A proper sales funnel allows marketers to understand the customer’s purchasing journey and anticipate their questions and doubts at various stages. These insights can be used to create and deliver relevant and timely marketing messages to the customer.
2. Marketing and sales alignment
If a customer has questions and can’t reach a salesperson because they are too high up in the funnel, they can still receive the information they want through marketing outreach.
An effective sales funnel allows marketers to answer the customer’s product/service questions without involving a salesperson that early in the process.
3. Time and effort savings
A good sales funnel allows marketers to filter out bad sales leads early on and focus precious marketing dollars only on leads with the highest likelihood of converting into paying customers.
Content marketing for every stage of the sales funnel
A content marketing strategy is integral to the success of your digital marketing sales funnels. Cold calling and aggressive outbound marketing strategies are no longer a sure route to success. The modern consumer wants to find a business organically of their own volition.
As such, having a comprehensive mix of content styles for each stage of the customer journey ensures qualified leads can access the right material at the right time.
It’s worth noting that this content marketing model is simplified, and the buyer journey isn’t always linear. Consumers might read a white paper before becoming aware of your company or receive a recommendation from a friend that leads them to your conversion content. This is simply one path a buyer can take to purchase.
Below are the stages of a standard sales funnel and the ideal content for each section.
1. Awareness stage
The goal at the top of the funnel is to build brand awareness. Your content marketing efforts should be designed to attract and educate buyers on their problems so you appear as an expert in your sector. This will encourage the prospect to engage with your brand. Potential content includes:
- Blog posts
- Social media content (Instagram, Facebook, TikTok)
- Search engine optimisation-driven content
- Videos, infographics, and visual content
The aim is to inform prospective customers of your brand and encourage them to explore your site.
For example, a customer may find your content on Google via an SEO-led blog post that addresses a problem they are having. After providing valuable content that answers their question, you could link to a video or whitepaper that provides more information on the subject.
This encourages the customer to explore your catalogue, piquing their interest and guiding them to the next stage in the funnel.
2. Interest stage
At this stage, the website visitor knows your brand and wants to discover more about their problem. They are curious and want to find out about the solution you have on offer. As such, suitable content includes:
- Blog posts
- Downloadable content (PDFs, eBooks)
- Whitepapers (especially for B2B audiences)
- Website content (landing pages)
- Email newsletters/drip campaign
Your lead isn’t ready to buy yet, but they want to learn more about your business. The goal here is to provide a wide range of content so that customers can learn about your brand in a way that suits them.
Some prefer to read in-depth whitepapers and eBooks. Others may like visual and video content. The more versatile your catalogue, the more opportunities you have to foster a strong connection with your audience and make them see you as a potential solution to their problem. This, ultimately, will result in generated leads.
3. Evaluation stage
At this stage, the customer knows your brand and trusts your expertise. Now, they will begin to assess whether you are a viable solution to their problem. This means researching solutions and reading up on the benefits of your service to see if you are the right choice. Ideal content includes:
- Customer stories and testimonials
- Case studies
- Comparison tables
- Product demos
- Webinars
At this stage, your content marketing tactics aim to make your brand look like a clear choice over the competition. They should be able to read customer success stories, view case studies, and see demonstrations of your product that act as social proof your solution is the best available. This will push them further down the sales funnel into the decision stage.
4. Negotiation decision stage
At this stage, the customer is convinced that your solution fits their problem well and is ready to buy. But they still need to decide to part with their money. The goal with content at this stage is to remove barriers preventing your customer from making a purchase. Suitable content includes:
- FAQs
- Contact information for customer support
- Live chat
- Free trials
- Limited time offers
Each of these content styles helps the buyer overcome a barrier they may face when deciding whether to buy. FAQs and customer support can answer any remaining questions the buyer may have.
Limited-time offers overcome price barriers. Free trials make the purchase feel non-committal. By removing these roadblocks, you alleviate doubt and decide to purchase clearer for your lead.
5. Renewal or repurchase
Once the buyer makes a purchase, the business’s goal shifts. Now, they need to maintain strong customer relationships and convince buyers to remain loyal to the brand for the long term. Ideal content includes:
- Exclusive content for buyers
- Exclusive communities on Slack, Facebook, LinkedIn, or Discord
- Loyalty programs
- Personalised email chains
- How-to guides
- Live workshops
- Partner program
- Product updates
Each content style shows your customers that you value them and haven’t forgotten them now that they’ve made a purchase. They also invite happy customers into a community that they can engage with.
This helps the customer connect emotionally with your business, fostering brand loyalty. This also encourages a current customer to recommend your brand to their colleagues, friends, and family. The customer lifecycle can then begin again.
B2C sales funnels vs B2B sales funnels
The content a potential buyer consumes and the path that buyer takes to purchase is heavily influenced by whether you sell to consumers or other businesses.
B2C sales funnels
B2C businesses usually target individuals. The buyer persona is most often that of a single decision-maker. As such, the targeted customers are likelier to make purchase decisions based on personal preferences and immediate benefits.
Time is frequently a concern, so consumers value fast, visual content they can engage with. They are less likely to take the time to read in-depth content or download comprehensive documents to make their decision.
The sales cycle is often shorter, with fewer touchpoints when compared with the B2B sales funnel. This includes:
- Longer decision process: B2B sales cycles tend to be longer as they often involve multiple decision-makers and more thorough decision-making processes.
- Focused content: Content should be more detailed and informative to support decision-making. For example, providing thorough white papers and insightful webinars can help establish your business as a trusted industry expert.
Lead generation strategies include:
- White papers and eBooks: In-depth reports or guides that address industry-specific challenges and provide valuable solutions.
- Webinars: Educational sessions that offer insights into complex topics and establish your company as a thought leader.
- Case studies: Detailed success stories of how your product or service has helped other businesses solve specific problems.
- Live chat: Real-time assistance on your website to answer queries and engage with potential clients directly.
At the beginning of the sales pipeline, you should focus on informal, emotional content that addresses your buyer’s authentic problems. Rather than prioritising complex, in-depth research, start small with social media marketing, infographics, videos, and short-form blog content.
When evaluating your product to determine the right choice, the B2C sales funnel should prioritise the benefits consumers will achieve when they buy the solution. It should put emotion front and centre. Show how the audience will feel and the lifestyle they will live when they buy.
Closing deals with a B2C audience is all about social proof. Consumers want to read reviews and decide for themselves based on the information available to them. It’s important to feature testimonials and FAQs to allow a buyer to reach their conclusions.
B2B sales funnels
For the B2B sales funnel, you target professional leaders, stakeholders, and executives. As such, their decision-making process is considerably more complex. B2B consumers are not likely to make an impulsive purchase decision. Instead, decisions are based on business needs and potential return on investment.
With this in mind, you should align your sales funnel to include content that reflects a B2B consumer’s needs. At the start of the sales pipeline, when the goal is building awareness, you should prioritise concise, formal, expert-led content demonstrating your expertise in your sector. This includes:
- Shorter decision process: B2C sales cycles are typically shorter as consumers make faster purchasing decisions based on personal needs and preferences.
- Engaging content: Content should be engaging, visually appealing, and easy to consume. This includes social media posts, videos, and blog articles designed to capture attention quickly.
Lead generation strategies include:
- Social media contests: Running contests on platforms like Instagram or Facebook to increase brand awareness and engage users.
- Free trials: Free trials or samples to let consumers experience the product before making a purchase decision.
- Email campaigns: Sending personalised offers, product updates, and promotional content to keep the brand top-of-mind and encourage conversions.
- Push notifications: Push notifications to alert users about special offers, new products, or important updates directly on their devices.
- Affiliate marketing: Using partnerships with affiliates to reach new audiences and drive sales through commissions.
Blog posts can still be integral to this stage but should be adapted to provide detailed information on expert topics. This differs from building awareness with a B2C audience, where content can be more emotional and personal.
For the B2B consumer, it’s also important to back up blog content with whitepapers and case studies. Doing so will prove you are both a trustworthy source and a thought leader in your industry: two characteristics businesses look for when choosing a solution.

Because of the complexity of B2B decision-making, the buyer journey to the bottom of the funnel can be longer, with more emphasis on evaluation and negotiation.
While B2C consumers may purchase after viewing your landing page and reading customer testimonials, a B2B buyer may seek further information and require live product demonstrations and meetings. It’s important to have the resources to facilitate these requirements.
To close the deal with a B2B audience, businesses should focus on providing personal support to the customer. Businesses want to feel like their needs will be catered to and value open communication.
Prioritise fostering long-lasting relationships where each party feels like an equal. Hold personal meetings and detail clearly how your partnership will be beneficial. This honest communication will turn a B2B consumer into a loyal customer.
Our B2B marketing automation tool lets you discover and nurture leads. It offers intelligent features to create personalised content for every sales pipeline stage and build stronger connections with your audience.
How to define your ideal customer profile?
Identifying your ideal customer profile (ICP) is crucial for tailoring your sales funnel to engage with your target audience effectively. An ICP is a detailed description of your most valuable customers, including their demographics, firmographics, and psychographics.
To map your customer journey effectively, you first need to understand your ideal customer profile. This will allow you to tailor your marketing strategies to the right audience, leading to a better customer experience and higher conversion rates. Here’s how you can go about doing this:
Step 1: Analyse your current customer base
Start by identifying the common traits among your best clients. Look at demographic information, purchase behaviour, and customer lifecycle stages. Automation software and CRM tools will be used to gather and analyse this data effectively.
Step 2: Identify key characteristics
Determine the demographic, geographic, and psychographic attributes that define your ideal customers. This includes age, gender, location, interests, and buying behaviours. Consider the unique pain points and needs your product or service addresses for these customers.
Step 3: Conduct market research
Gather insights through market research, including industry reports, competitor analysis, and trend studies. This helps you understand the broader market landscape and more accurately define your buyer persona.
Step 4: Collect customer feedback
Use customer surveys, interviews, and feedback forms to gain direct insights from your audience. This qualitative data complements your quantitative analysis and provides a well-rounded view of customer preferences and behaviour.
But don’t stop there. You can also collect feedback from your sales teams and valuable insights about common questions high-value customers ask.
Here’s a pro tip: Use this data to create an internal knowledge base for your sales reps. Additionally, you can use this information for your customer support and FAQ pages.
Step 5: Create buyer personas
Develop detailed buyer personas that represent your ideal customers. These personas should include specific information such as job titles, challenges, goals, and preferred communication channels.

Source: Salesforce
Content marketing, such as engagement with blog posts and social media, will help you refine these personas. To define your ideal customer, you can gather data through various methods:
- Market research: Conduct market research to identify trends, patterns, and insights about your target audience. This can include analysing industry reports, social media analytics, and customer feedback.
- Customer surveys: Conduct surveys among your existing happy customers to gather information about their demographics, firmographics, and psychographics. This can include questions about their job roles, industries, company sizes, and pain points.
- Customer feedback: Analyse customer feedback from various channels, such as reviews, ratings, and support tickets. This can provide valuable insights into customer needs and expectations.
- Social media analytics: Analyse social media analytics to understand your audience demographics, interests, and behaviours. This can help you identify patterns and trends in your target audience.
Step 6: Use data and analytics
Continuously monitor and update your ideal customer profile using data from Google Analytics, CRM systems, Sales Analytics, and other management software. This will help you adapt to changing market trends and customer behaviours. Measure the success by tracking key funnel metrics, like lead conversion and customer retention rates.
Benefits of defining your ideal customer
Defining your ideal customer profile provides several benefits, such as:
- Personalised messaging: By understanding your ideal customer, you can create personalised messaging that resonates with them, increasing the effectiveness of your marketing and sales efforts.
- Targeted content: Tailoring your content to your ideal customer helps ensure your message reaches the right audience, reducing waste and improving engagement.
- Improved sales: By understanding your ideal customer’s needs and pain points, your sales team can better address these issues, increasing the chances of conversion.
- Enhanced customer experience: Defining your ideal customer helps create a more tailored customer experience, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Generate leads: With a well-defined ideal customer profile, you can generate leads more effectively through targeted marketing campaigns and lead nurturing strategies.
- Business growth: Focusing on your ideal customer segment can drive business growth by attracting and retaining high-value customers.
- Optimise your funnels: Understanding your ideal customer’s buyer journey and pain points allows you to optimise your sales funnel for better conversion rates.
- Brand awareness: Creating content marketing campaigns tailored to your ideal customer can help build brand awareness and establish your brand as a trusted authority in your industry.
How can I quickly build and nurture a sales funnel?
Building a sales funnel doesn’t have to be a very time-intensive effort. With a little bit of understanding, you can build and maintain a sales funnel that will allow you to identify and harvest quality leads again and again.
Building a sales funnel is all about knowing your leads, prospects, and customers, engaging them in a timely and relevant manner, and following up diligently:
Step 1: Analyse your existing customers
A good sales funnel is built on deeply understanding your existing customers. The more customer data you can gather and analyse, the more effective your sales funnel will be.
You can gather customer data by actively communicating, tracking their interactions with your digital and offline presence, and segmenting customers.
- Targeted campaigns: Segment your audience based on behaviour, demographics, and other relevant factors to deliver more personalised and effective marketing messages.
- Lead scoring: Implement lead scoring models to prioritise and focus on high-quality leads, ensuring your sales efforts are directed towards those most likely to convert.
An analysis of your customers should include their pain points, needs, goals, aspirations, and past solutions. Using this data, you can find lookalike audiences and put out the right messaging at the right time to attract prospects.
Step 2: Captivate your target audience
Your audience will likely be distracted by the multiplicity of demands on their attention. You need to capture their attention across online and offline platforms to compel them into your sales funnel.
Use compelling content that educates and informs prospects, assures them that their needs are known and will be met, and hooks them into asking for more information. Enhance their user experience by:
- Ensure your website and landing pages provide a smooth and intuitive user experience, reducing friction at each funnel stage.
- Your website is optimised for mobile. With the growing number of mobile users, ensure your digital assets are optimised for mobile devices to capture and convert leads effectively.
The content to capture your audience’s attention can be organic (non-paid social media posts, blog posts, email newsletters, SEO) and paid (social media advertising, targeted keywords, influencer content). Find ways to align this content and related campaigns with the interests and needs of your target audience.
Step 3: Nurture leads through your digital marketing channels
Implementing various digital marketing channels effectively at different funnel stages is key to nurturing leads. For example:
- Awareness stage: Implement SEO strategies and content marketing, such as blog posts, to increase brand awareness and attract potential buyers through organic search.
- Consideration stage: Use social media ads and retargeting to keep your brand top-of-mind with prospects who have shown interest but are not yet ready to convert. Engaging content like webinars and case studies can help nurture these leads further.
- Decision stage: Email marketing campaigns can provide personalised offers and reminders to leads close to purchasing. Detailed product demos and customer stories can also help convince prospects to take the final step.
Step 4: Create a great landing page
All your content should typically lead your prospects somewhere, such as a landing page. This is where you make your first impression. A great landing page communicates who you are as a company, your offerings, and what needs you can solve.
Landing pages can also entice visitors with offers and should be used to capture contact data like email addresses. Lastly, but very importantly, landing pages should have a clear call-to-action that takes the prospect further down the sales funnel.
Step 5: Create a powerful email campaign
Having captured email information from your leads, keep them engaged with a powerful email campaign. A good email campaign starts by informing and educating leads, and helping them understand how your products and services can meet their needs.
Only then should it progress to offering your leads offers that compel them to convert into paying customers. Focus on inspiring leads to become customers instead of just bombarding them with crude product pitches.
6. Keep following up
When a customer purchases your products and services, they don’t move out of the sales funnel. Instead, they stay at the bottom of the funnel, and you want to keep them there.
These customers have paid for and used your products and services, and you want them to return for more. Keep them engaged with recurring communication. Thank them for their purchase and incentivise them to return through promotional (offers) and informational (new product information) campaigns.
Your sales funnel is a dynamic tool; feel free to tweak it in response to changes in the market and your company’s offerings. It is important to have a sales funnel that captures the widest number of prospects and effectively narrows them down to a smaller pool of loyal customers.
Examples of a sales funnel

Imagine a sales funnel for a company that manufactures, markets, and sells stylish furniture online. The company knows that most customers are 30-40-year-olds who spend much time online, specifically on visual social media platforms like Instagram.
The company runs a series of Instagram Ads using compelling content targeted at potential audiences aged between 30 and 40 years. The Instagram Ads route users to the company’s landing page, where a pop-up encourages them to sign up for its newsletter to receive tips, updates, and, crucially, offers. The people who signed up have now become leads.
Over the next few weeks, these leads will be sent content that informs them about the company’s furniture designs and quality. The intent is to inspire them to redesign their personal spaces with this company’s furniture.
At the end of the email campaign, the company sends these leads a discount coupon. Primed with ideas for their spaces, the discount coupon helps push the leads toward an actual purchase. After the purchase, the company doesn’t forget about these buyers. They become recipients of yet another email campaign with the same goals but different content.
And there you have it: a sales funnel. At the top, social media users were made aware of the company and its offerings and drawn into the funnel. Their interest was piqued, and they evaluated the offerings and decided to purchase the product. Hopefully, they will renew their relationship with the company by repurchasing.
Case study: Canva’s sales funnel
Australian graphic design platform Canva has a textbook omnichannel sales funnel that guides customers to try the platform and eventually upgrade to a Pro subscription.
For this case study, we’re posing as a consumer hosting a wedding but struggling to create an effective invitation. Let’s head to Google to find more information.
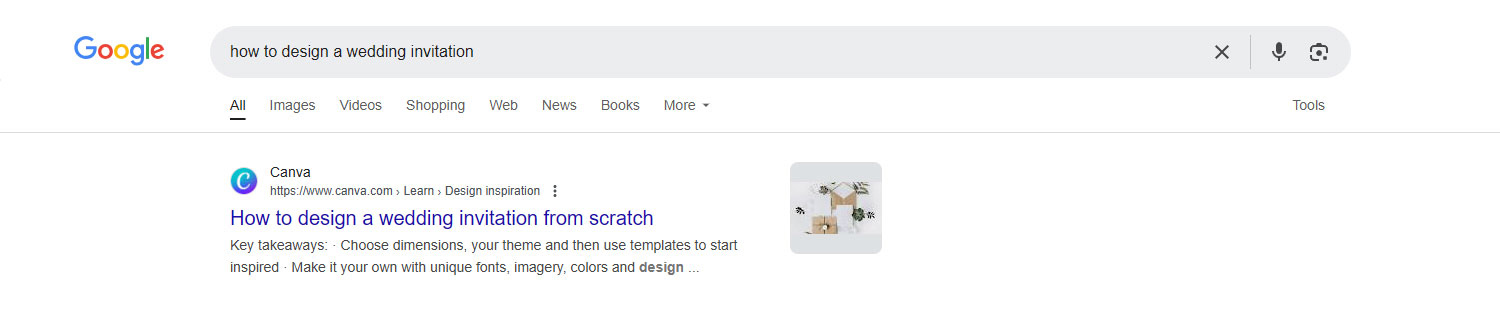
Canva’s blog, ‘How to design a wedding invitation from scratch,’ seems to have some advice we can use.
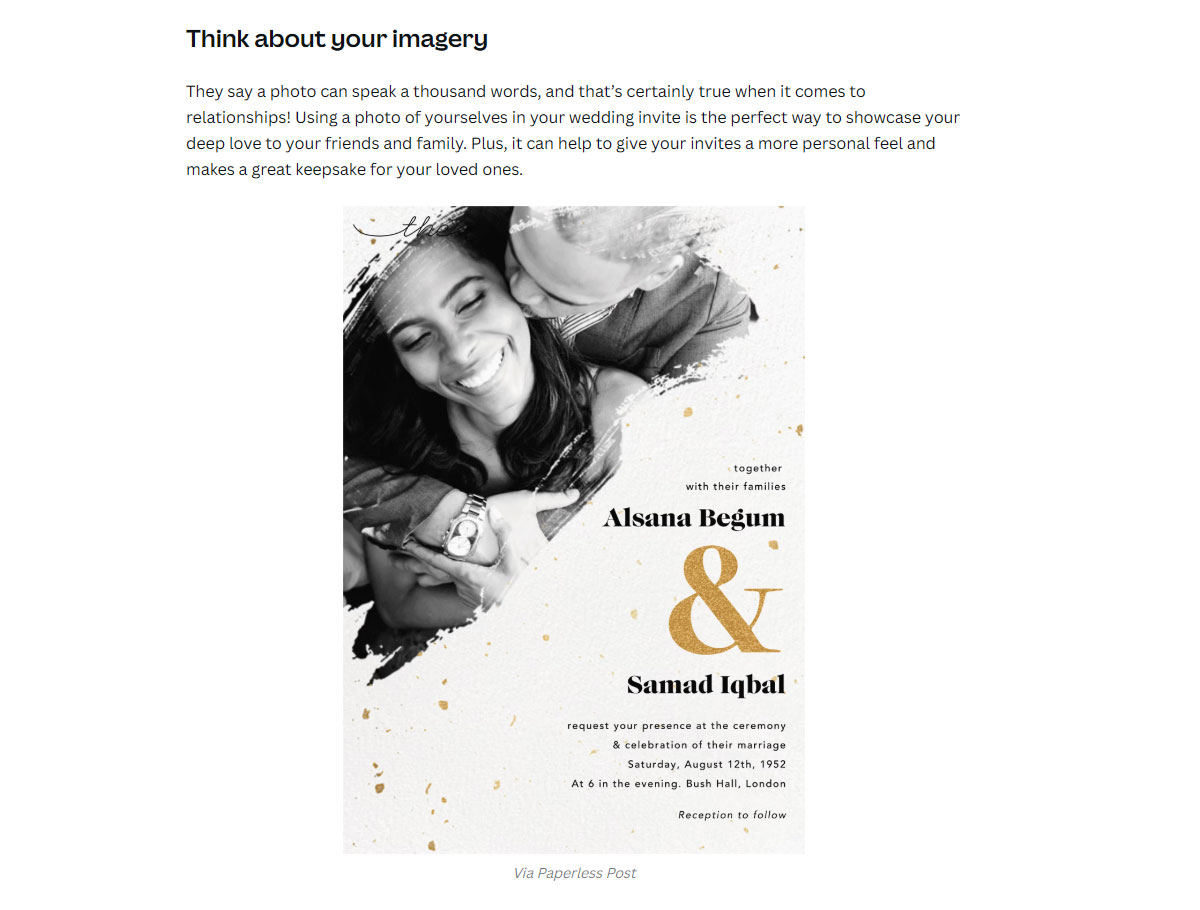
Source: Canva
The blog post contains nine excellent tips. It educates us on everything we need to consider when designing a wedding invitation. It feels personal and acknowledges how important the wedding day is. At this point, the customer feels like they’ve learned a lot.
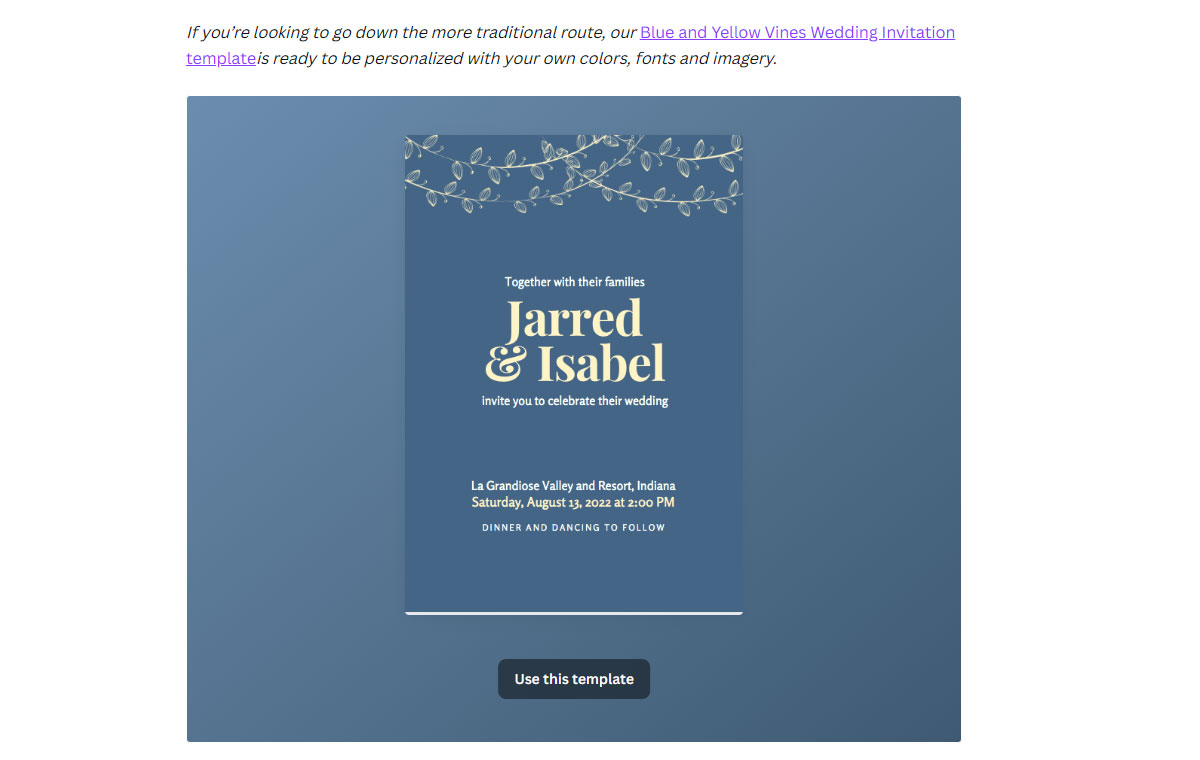
Source: Canva
Canva also expands on each tip by providing a template a customer can use to achieve the desired result. Each template has a ‘Use this template’ button that, when clicked, prompts a user to sign up.

Source: Canva
Once signed up, the user can access the template and create their design. As this is completely free, the user can design their invitation without paying any money. The consumer is now firmly in the interest stage.
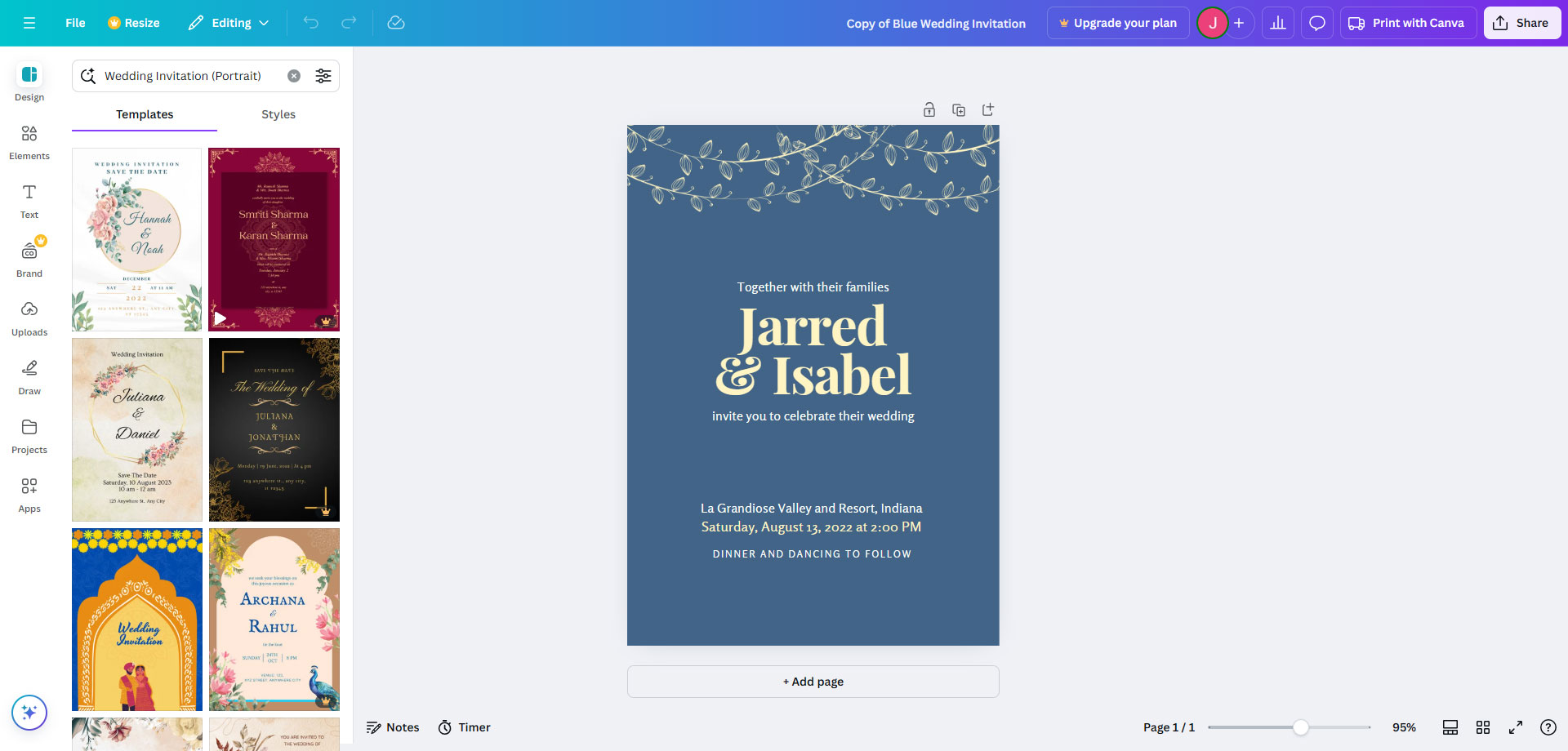
When experimenting with the service during the interest stage, they may use a font or template with a ‘crown symbol’ next to it. These elements are locked behind the Canva Pro paywall. Clicking this opens a pop-up telling the user they need to upgrade to use the feature.
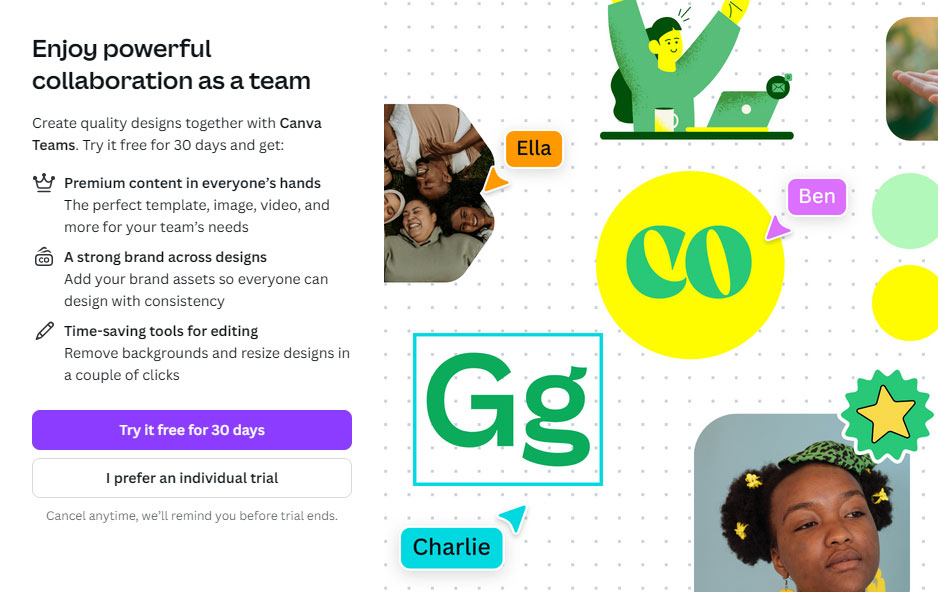
The content includes three of the core benefits of Canva Pro and a call to action to try it for free for 30 days (with a note that they can cancel any time).
The chance to unlock new fonts alongside the promise of a free trial could be enough to convince many customers to upgrade. But let’s assume we aren’t convinced and want to learn more about Canva before buying. Let’s return to the blog.
“With so many expenses involved in planning your nuptials, you may want to design your own wedding invitations to keep costs down. As an added bonus, it also adds a more personal touch. The good news is, you don’t have to be a professional designer to create gorgeous invitations that perfectly embody your one-of-a-kind relationship. Or, if you’re known as the ‘creative’ friend or family member and have been tasked with designing the invites, you don’t have to procrastinate while avoiding your blank canvas. We even have a free video guide on how to design your wedding invitations for free.”
Canva also includes internal blog links to move the consumer from the awareness stage to the interest stage. The ‘wedding invitations’ internal link takes us to a landing page.
Here, Canva focuses on the benefits of its service. It reveals how customers can design and print wedding invitations within the platform.
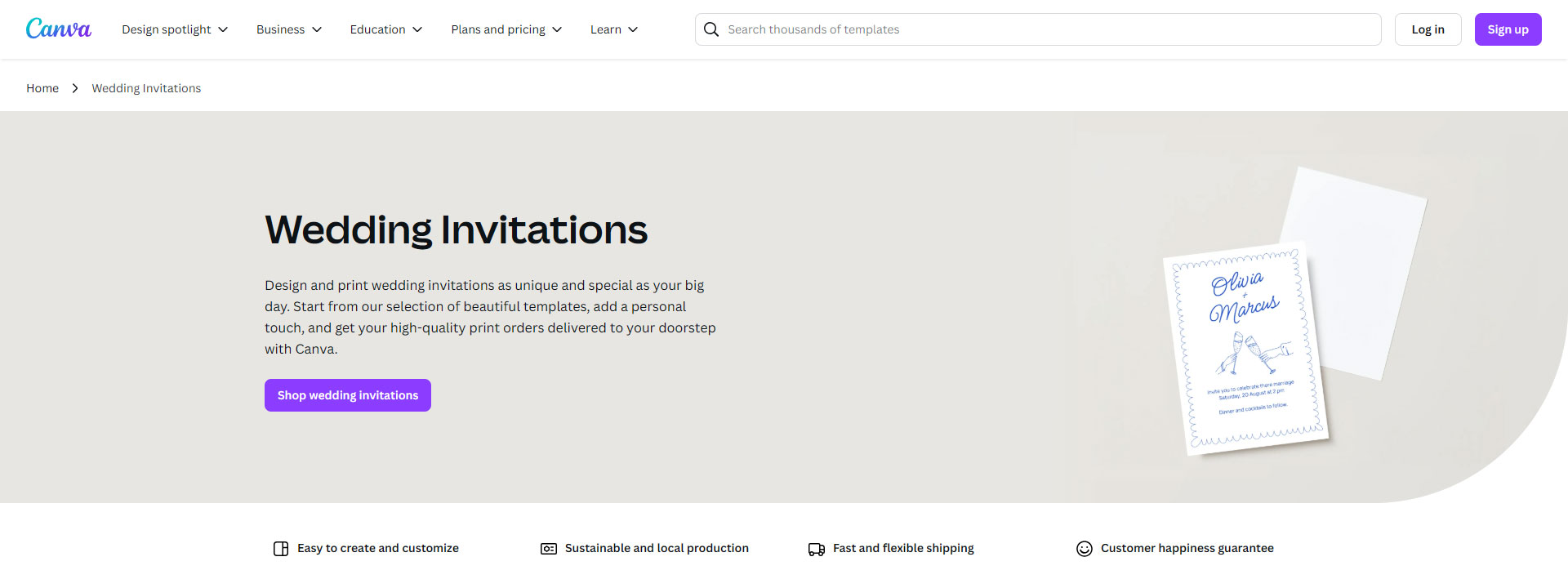
Source: Canva
Like the blog, this page also showcases dozens of potential templates that customers can click on. They will then be prompted to sign up and taken to the main interface where they can design their invitation.
The blog also links to an 11-minute YouTube video hosted by an expert. The video instructs customers to search for, customise, adapt and print a wedding invitation using Canva.
Source: YouTube
These elements guide the customer down the sales funnel from awareness through interest to the evaluation stage, where they genuinely see Canva as a solution to their problem.
But what exactly is Canva’s evaluation stage content? Well, it’s the platform itself. This is the key to their success. Ultimately, all roads within Canva lead consumers to try out the platform for themselves. There are many free templates, so a user has thousands of options. Once users are in the design platform, they can try out all the core features they like.
Canva’s business model is based on the depth of its Pro package. Many of the best fonts, templates, and elements are locked behind the company’s paywall. As long as the user enjoys the platform’s free version and continues to use it, it is only a matter of time before they decide to subscribe to unlock the full range of features.
You can see how Canva’s targeted content all ties together. The path isn’t linear. Some users may try a free template immediately. Others may click the internal links to read more about Canva’s wedding invitations.
Some may watch the video linked within the blog. But every path eventually leads a customer to test out the platform and, at some point, try out the Pro subscription.
This is the crux of successful omnichannel digital marketing and lead nurturing. It provides a seamless customer experience wherein customers can consume the content they want and take any path to purchase.
Measuring a sales funnel’s success
Marketers should also actively tweak their sales funnel based on its performance. A sales funnel is a dynamic tool that’s likely to change in shape and size as your business grows:
- You understand your customers’ needs better as these needs evolve and your product and service lines diversify.
- A good sales funnel is regularly changed in response to evolving business environments.
A key metric to track when evaluating sales funnels is the conversion rate: how many visitors are being converted into leads, how many leads are into prospects, and how many prospects are into paying customers?
Understanding these conversion rates will allow you to pinch or expand the funnel in relevant places and eventually arrive at a shape that maximises conversions.
Ready to set up and automate your sales funnel?
Salesforce Cloud can help you



Optimising the sales funnel
The best way to optimise your sales funnel is to try different things and track the resulting changes in conversion rates. The points at which visitors convert into leads leads into prospects, and prospects into customers are crucial.
Marketers need to ensure that the content and the sales activities they use at these points are highly effective. Several methodologies and tools can be used to achieve this result. Let’s look at two.
1. A/B testing
A good way to measure effectiveness is to run A/B testing campaigns. Let’s go back to the example of our direct-to-consumer furniture brand. To optimise their sales funnel, the marketing team could run several Instagram Ads and check their performance before settling on the most successful one. They should also run A/B testing on their landing page, where visitors are converted to leads, and prospects are converted to customers on their email campaigns.
This can involve:
- Landing pages: Test different headlines, images, and calls to action (CTAs) on your landing pages to see what resonates best with your audience.
- Calls to action: Experiment with various CTAs in your emails, blog posts, and social media ads to determine which prompts generate the highest engagement and conversions.
- Content variations: Try different formats and messages in your content marketing efforts, like video versus text or long-form versus short-form content, to see which performs better.
A/B testing is superior because it eliminates subjectivity and provides a growing bank of data that you utilise to make future decisions. The method is also only limited by your creativity. You can and should test every type of content to determine which types are most effective.
At the awareness and discovery stage, for example, a business can run the same ads on Instagram and Facebook to see where they perform better. Having found that Facebook Ads bring in more traffic, they could publish the same ads while changing different components (headers, images, body copy) to see which drives better click-through rates.
Targeted emails are also a goldmine of insight for the A/B tester because they are extremely easy to adapt and test. Businesses could write five emails about the same topic with the same goal, sending each out to different customer segments within the customer base to view which receives the most opens and responses. The “winner” can then be analysed and explored to determine why it was most successful.
All of these approaches provide a valuable knowledge base that you can use to make better data-backed decisions. Still, you should never sit back once you think you have ‘the winning formula.’
It’s important to continuously test and optimise your digital marketing funnel to stay at the forefront of consumer preferences and industry changes. Optimising your sales funnel is a constant cycle of testing and incorporating the results.
2. Sales funnel management software
Several tools exist to assist with sales automation and lead management. For example, you could utilise a sales funnel tracking solution to view your pipeline in real time.
This is especially useful for collecting quantifiable sales data that you can use to identify gaps in your current funnel. Google Analytics can also help by allowing you to track metrics such as conversion and click-through rates.
Similarly, CRM tools are a helpful way to keep customers on board at every stage of the funnel. Our Sales Engagement tool, for example, lets you automate essential tasks such as email follow-ups and meeting bookings. Utilise tools and software:
- CRM systems: Implement Salesforce CRM software to manage and analyse customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. This helps maintain strong customer relationships and ensures no lead falls through the cracks.
- Marketing automation: Use Salesforce marketing automation platforms for tasks like drip campaigns, lead scoring, and personalised email marketing. These tools can streamline your processes and improve efficiency.
- Sales automation: Salesforce sales automation tools can handle repetitive tasks, such as follow-ups and meeting scheduling, so your sales team can focus on more strategic activities.
You can leverage AI to instantly identify your strongest leads and those most likely to close. That means you can decide where to prioritise your customer retention efforts to provide a great user experience to those you risk losing.
3. Track everything
Ultimately, optimising a sales funnel for your business is a long-term strategy. You require data to optimise your funnels over time. A/B testing and sales pipeline management tools can help gather this data, but you still need to put it to use. Some key metrics to track:
- Conversion rates: Monitor the conversion rates at each stage of the funnel, from awareness to purchase, to identify any drop-offs and areas for improvement.
- Customer journey analytics: Use tools like Google Analytics to track how users move through your funnel and where they might get stuck.
- Funnel metrics: Regularly review key metrics such as lead generation rates, click-through rates, and sales conversion rates to understand the effectiveness of your sales funnel and make data-driven adjustments.
It’s important to allot time to measure the success of your funnel and explore what the information you possess is revealing. High click-through rates but a low sales conversion rate may show a weakness with your content in the middle of the funnel.
A lack of repeat buyers reveals you should spend more time on post-sale content that promotes brand loyalty. Using these funnel metrics, you can strengthen and define your sales funnel over time.
Sales funnels work best when built with specific goals for defined target audiences and are executed using compelling marketing content. Without these three basic tenets, sales funnels are leaky, letting out prospects and leads before converting them into paying customers.
How Salesforce can help?
If you are trying to build a sales funnel for your organisation or optimise the one that you have, Salesforce Solutions can help you. Here’s how:
Pardot, our B2B marketing automation tool, enables you to fill your sales funnel with high-quality leads and intelligently nurture them. With it, you can create beautiful landing pages, forms, and email campaigns to personalise customer engagement.
With our contact management tool, marketers and salespeople have an ever-present snapshot of customers. Meanwhile, our opportunity management capability helps you close deals faster by connecting you to the people and information you need. The Salesforce Engage tool lets you draft and send personalised communications to customers with just one click. It also helps you maintain and view a detailed history of prospect or customer interactions.
Powerful reports and dashboards help you ensure that all your sales and marketing decisions, including building and optimising your sales funnel, are data-driven and well-informed.