Design next-gen clinical trials with data and AI
Discover how these technologies can help streamline processes, increase efficiency, and get therapies to market (and patients) faster.

Today’s clinical trial teams face more barriers than ever before. From burdensome documentation to manual processes to increased regulatory hurdles, modern trials are more complex and less efficient. This complexity affects trial design, leads to suboptimal study operations at sites, and makes enrolling, engaging, and retaining the right patients difficult and expensive.
Until recently, the industry has tried to address these inefficiencies through the digitization of existing clinical processes. The hope was that this would reduce documentation and create a more orderly system. However, digitization alone has not been enough. Effecting truly meaningful change in the clinical trial process requires more than just moving from paper and spreadsheets to digital systems. It requires that the industry consider transforming the key processes themselves, namely trial design, site selection, and recruitment and retention efforts.

Bringing data together paves the way for AI.
As life sciences organizations set themselves up for an AI driven future, it's important they ensure there’s a well oiled data operation in place.
Most life sciences organizations have data spread across many sources: healthcare systems, EHRs, lab systems, personal digital health, medical device systems, and particularly important in this instance, clinical trial systems. This will only continue to grow, creating more and more complexity as we go forward. It's not just the abundance of data that’s driving complexity, but also that it’s siloed across disparate systems, making it difficult to access and activate.
Creating a foundation of connected data is a worthwhile investment. It will enable you to gain valuable patient and therapy insights, streamline clinical, medical, and commercial processes, and innovate faster. And though data unification may seem overwhelming, the right suite of tools and solutions can streamline the process, enabling your organization to be up and running sooner rather than later.
Data unification and standardization is typically done through an integration layer like Salesforce’s MuleSoft. The benefit of an integration layer is that it provides strong APIs that can help not only connect data, but also provide access and properly map it to a unified clinical data model. When doing this, it’s best to use a suite of technology that can work together. This will enable you to get the most out of your solutions. For example, in the case of Salesforce, Data Cloud and Life Sciences Cloud are built on top of the Einstein 1 platform. This means that all data that’s pulled in can easily and automatically be plugged into the life sciences apps, powered by AI, and delivered as insights, next best actions, and productivity boosts to both clinical sites and study teams.
Powering better clinical trials with Life Sciences Cloud
Bringing your data together provides context. It allows all parties (sponsors, site administrators, study teams, etc.) to operate from one single source of truth. This enables study teams and clinical operations personnel to quickly ascertain what sites and study processes are effective and where there might be opportunities for optimization.
Access up-to-date, real-time information without sacrificing patient privacy.
Giving all parties access to the information they need enables new levels of transparency. This is especially true for sponsors who often have a difficult time getting a window into what’s happening at their sites. A platform like Life Sciences Cloud provides a de-identified aggregate view made up of anonymized data points to give sponsors insight into things like individual site recruitment, patient response, and overall trial progression.
Ease administrative burdens throughout the entirety of the trial.
One of the biggest burdens (and slow-downs) in a clinical trial is the need to revisit all affected downstream processes and system configurations every time a change is made. We are not far off from a future in which technology might be able to solve this challenge. A unified platform could ensure that any data changes or updates cascade across all systems. This would mean that if something changes in the study protocol documents, it would also change in all related documents, thereby ensuring that documentation is up-to-date across all parties. And because this would happen automatically, no extra time or administrative strain would be placed on the timeline or trial team.
Power a stronger, more capable AI operation.
Your AI is only as good as the data from which it draws. Putting all your data in one place optimizes your AI capabilities. Better AI equals better outcomes across the board, from reducing risks due to manual error to improving stakeholder management to bringing life-saving devices and therapies to market (and patients) faster.
The value of AI throughout the clinical trial lifespan cannot be overstated. Employing it throughout each trial stage makes it possible for teams to overcome common challenges and allows organizations to:
- Enable better study design
- Improve site selection
- Enhance patient recruitment, enrollment, and engagement
Design better studies with data and AI.
Designing a clinical trial is no easy feat. Often described as part science, part art, it is a highly collaborative and iterative process.
Historically, clinical trial systems have followed a serial or waterfall process rather than supporting the flexible and agile processes needed for the protocol amendments, downstream processes, and ongoing changes that happen throughout the course of a typical trial. For example, the study protocol that’s designed and drafted at the beginning of the trial often needs to be amended to address operational feasibility, patient population realities, or for scientific rigor once the study is underway. And because the nature of clinical trials is that no trial gets it “right” the first time, redundancies are often baked in, necessitating that downstream processes be revisited and documents and systems be updated. Instilling automation and AI throughout the clinical trial journey can help teams overcome these challenges by making it possible for them to pivot faster, update downstream processes more easily, and run more flexible and agile trials.
Transforming the trial design process into something more automated and data-driven starts with bringing data together. A holistic, unified view allows everyone to access important information and enables you to better know and understand patient populations.
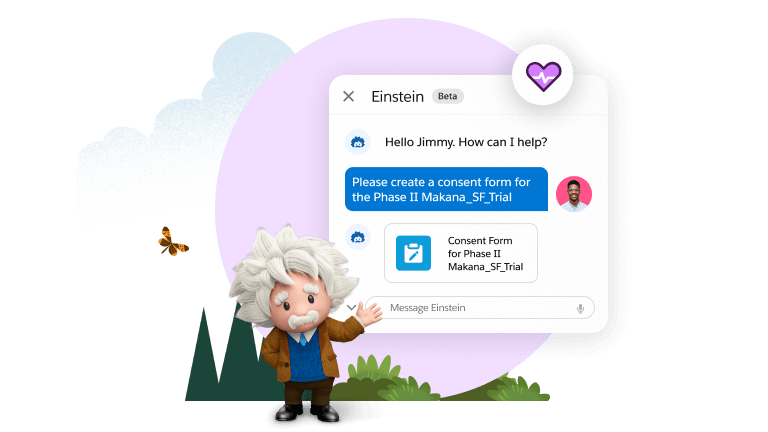
Having a single source of truth not only provides insight, it makes it possible to use generative AI to combine those insights with patient population analysis, historical data regarding the success or failure of past study designs, and operational feasibility to create a much more efficient, data-driven study design. This replaces the time-consuming manual efforts traditionally needed to ensure that studies are designed well. Even further, the same AI-powered tools can also be used to streamline the process of drafting other study documents including site contracts, consent forms, study feasibility questionnaires, and even regulatory documents.
This is a huge productivity gain. It also makes for a more agile, flexible, and iterative study process. It enables teams to easily amend any documents (if and when that proves necessary), and use generative AI to easily identify all important data elements within them. Those data elements can then be used to automate and streamline downstream processes and activities like site feasibility questionnaires and the design of your electronic data capture (EDC) database.
Improve site selection with AI-powered site analysis and insights.
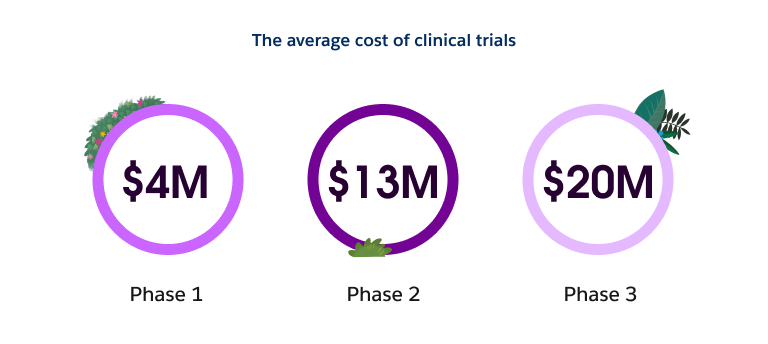
Technologies like AI and automation can help reduce these costs by shaping a more nimble process that enables clinical trial teams to make better initial decisions and pivot quickly when necessary. This is especially relevant as it relates to site selection.
Site selection is critical and difficult. Effectiveness between study sites can vary greatly, making the ability to choose the right sites highly consequential to the success of the overall trial. Despite this, site selection is not always performed in a scientific or entirely data-driven manner. At present the vast amount of site analysis is done manually. This not only takes time, it also fails to take advantage of the totality of data at an organization's disposal, thereby missing valuable insights into the potential effectiveness of selected sites.
Coupling a data-first approach with AI helps ensure you’re choosing the best possible site for each trial. Unlike manual analysis, AI models can be developed and fine-tuned based on the available past and current site performance data (both structured and unstructured). This includes characteristics that are often markers of a site’s ability to perform well — for example, enrollment rates, data entry timelines, data quality, and compliance to protocol. Having this data enables teams to quickly and easily identify risks associated with each site, ascertain why certain sites may be exhibiting those risks, and deduce which site(s) have the highest likelihood of success. You can then use this information to identify the best possible sites for each particular study. The ability to optimize your site selection in this manner may make it possible for you to choose fewer, more effective sites, ultimately reducing costs. The end result is the transformation of a once manual and cumbersome process into one that is data-driven, highly automated, and cost effective.
Enhance site management with AI.
Once sites have been selected, they must be closely managed throughout the course of the study to ensure both site and study success. This has generally been time-consuming and labor-intensive, but implementing predictive and generative AI tools can activate site data to help teams gain insight and quickly and easily identify markers of risk. For example, teams might use site data to build prompts that get them immediate answers to questions that once required a lot of manual research and analyses. This would enable them to ask the system (via an AI-driven prompt) “What are the five slowest enrolling sites in this last month?” They could even go one step further, and ask “what are the next best actions?” This would allow the team to understand what’s happening and provide the necessary assistance (training, recruitment, etc) to improve site performance. Alternatively, it could help them make the decision to close or replace certain sites quickly in an effort to maintain efficiencies and reduce costs.
Ultimately, the use of AI augments manual processes, eliminates guesswork, and streamlines site selection and site management throughout the trial. It allows you to zoom in and out as needed, making it possible to easily identify and address sites that are not enrolling on schedule, not adhering to diversity requirements, and generally exhibiting data quality issues. In this case, you would be able to pinpoint the issue at hand and then address it with the specific site in question. It enables you to help remedy the situation through things like additional training and/or recruitment support.
Ease the barrier to recruitment with AI-driven patient matching

Clinical trials need the ability to find the right candidates (and then keep them engaged and adherent throughout the duration of the trial). Unfortunately, things like lack of awareness, inability for patients to travel to sites, strict eligibility requirements, and competition between trials create barriers that are hard for life sciences organizations to overcome.
Further adding to these challenges, many life sciences organizations still run their recruitment operations manually (and on a trial-by-trial basis). This leaves teams going through patient lists, patient schedules, EMRs, and patient registries to find the right patients for each trial. This time-consuming process results in slower recruitment and enrollment rates.
While at present, recruitment success generally relies on multiple methods of recruitment, AI-powered patient matching can help clinicians and sites identify potential study participants much more easily. AI patient matching provides study teams with an intelligent, efficient, and accurate way to match prospective trial participants to eligible trials. It provides access to patient data from EMRs, enabling site personnel to use that data to fuel AI-driven patient identification. This negates the need to manually go through patient lists and frees up trial teams to focus on more valuable tasks. For example, teams could use AI pre-screen criteria to automatically identify prospective trial participants and generate lists of patients who are ready to be reached out to and recruited to join a clinical trial. Holistic patient profiles (created through integrated data) provide a 360-degree view of the patient and their healthcare data, which can then be used to “‘feed”’ AI-powered patient matching algorithms. This results in more accurate matches that ensure patients are paired with the trials that are most appropriate for them.

Individual engagement reduces drop-out and increases adherence
Finding the right patients is only the first step. Once a patient has come into a clinical trial, the focus pivots to making sure they stay in the trial and adhere to the protocol. Personalized engagement can go a long way toward increasing adherence and decreasing dropout.
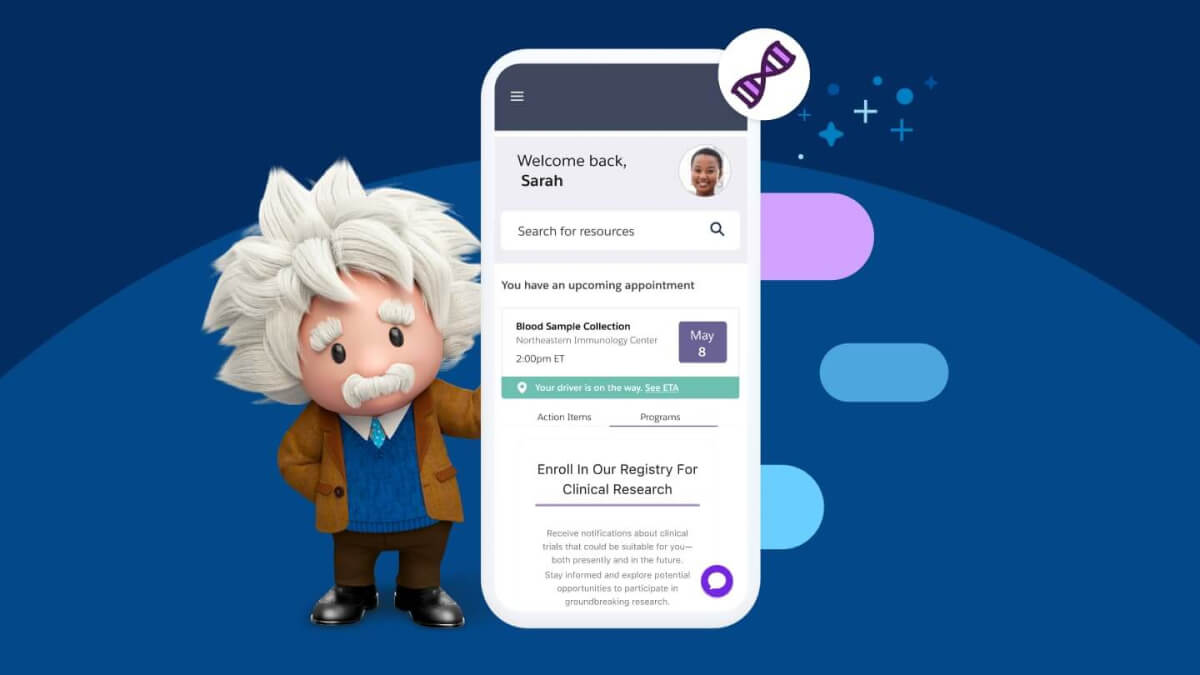
AI tools alongside a unified view enable the trial team to stay close to each and every patient. This ability to follow a patient from outreach through enrollment and beyond gives life sciences organizations insight into how that person engages, allowing them to identify personal preferences and behavior patterns. For example, do they prefer phone calls? Do they like chat messaging? Would they rather get emails? Tracking these behaviors and preferences can help teams identify next best actions that further personalize engagement. It can also allow them to understand and proactively identify where and when patients might be at risk for dropping out.
This type of always-on engagement is not only good for trial teams, it benefits the patients, too. A platform that’s available 24/7 provides people with the access and transparency they desire. Patient portals streamline the clinical trial process through participant management, which uses automatching and customized workflows to help get recruited trial participants onboarded quickly. This makes it faster to recruit, educate, and engage candidates throughout the study, lowering dropout rates and speeding up clinical trials overall.
Start delivering more efficient clinical trials and achieving better outcomes today
Data and AI are transforming the clinical development process, replacing the traditional waterfall approach with more iterative, agile processes that enable teams to operate in a more data-driven manner. An AI-powered, unified platform approach benefits every stage of the trial process, from site selection and management to recruitment and enrollment to engagement and retention. It puts all teams and stakeholders on the same page, enabling them to unlock efficiencies, reduce costs, and get therapies to market faster.

See our Accelerate R&D Innovation solution in action.
More Resources

Guide
Pharma Technology Playbook

Case Study
Creating a Platform to Drive Accelerated Patient Engagement

Webinar
Life Sciences Cloud Innovation